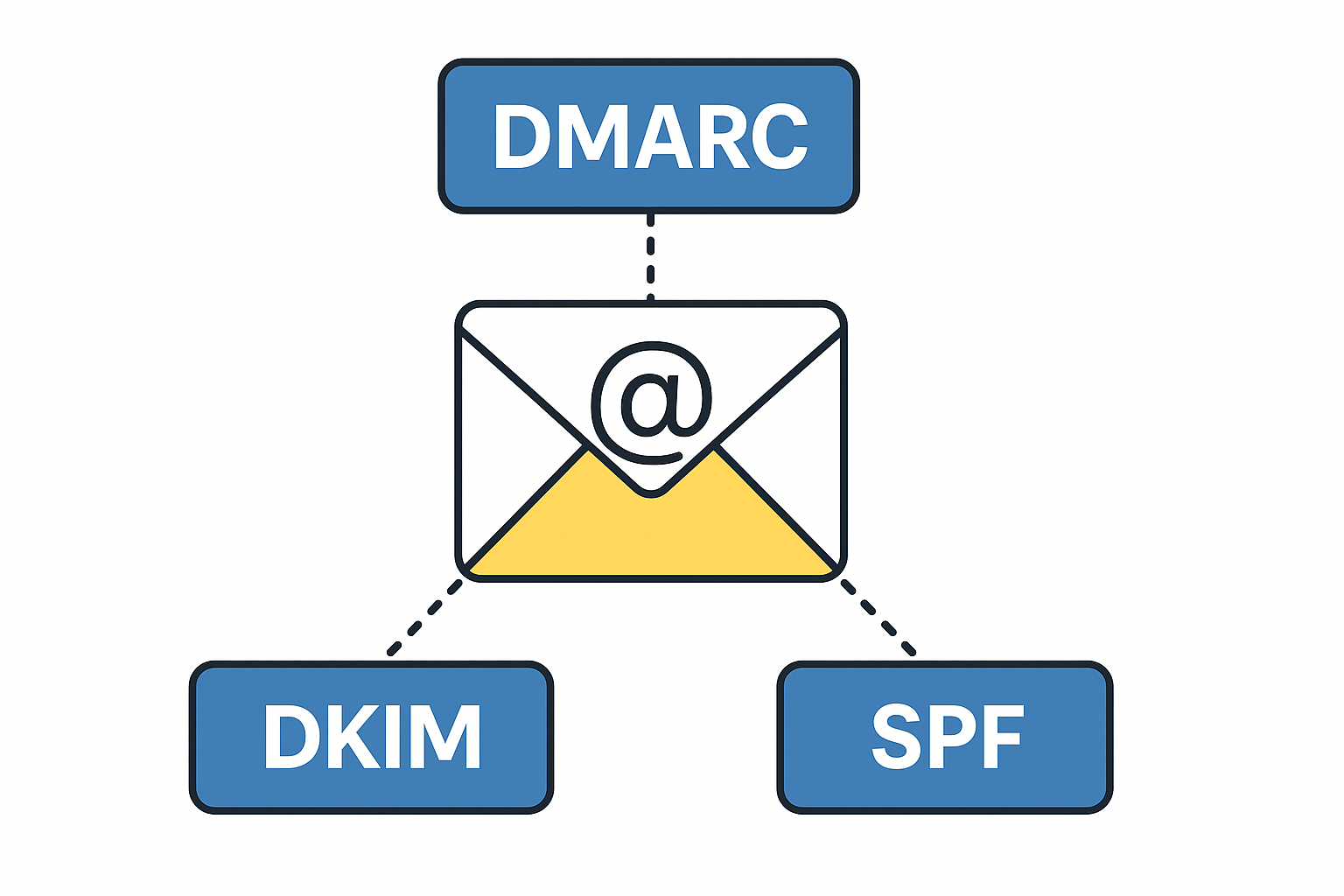
DMARC, DKIM and SPF are three separate email authentication protocols that build layers of security around email delivery and integrity. Used in conjunction with each other, they provide a durable layer of protection for inbound emails and brand protection to prevent bad actors from sending emails using your business domain name. These tools provide domain owners control over how email is handled if the email fails the authentication checks. Let’s walk through each in more detail.
The first step in the email authentication process is DKIM, which stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail. This tool digitally signs emails using cryptographic keys, so that the receiver can verify that the email came from where it claims it is from and provides assurance the email was not tampered with in transit. The reason why DKIM is used in combination with SPF and DMARC is that DKIM alone does not authenticate the “From” address.
The SPF / Sender Policy Framework is designed to confirm the IP address of the sending email server matches the SPF record stored in the DNS. If the SPF record’s IP address does not match the sending email server’s IP address, the message will not be delivered.
This tool protects against forged sender IP addresses, reduces your changes of phishing and increases email deliverability. As with DKIM, SPF does not verify the “From” address that users see. This is where DMARC enters the equation.
DMARC or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance is designed to handle the email in case of a fail after the SPF and DKIM process. If the email passes the DMARC process, the email can be delivered by the receiving email server. If the email fails, the receiving server DMARC policy dictates how the email is handled upon receipt, but failed the SPF and/or the DKIM process. Three options exist for the policy including none (monitor only), quarantine (send to the spam folder) and reject (block completely).
Almost all legitimate email providers require DMARC for business emails at this point for smooth email flow. Without DMARC, attackers can send emails pretending to be from your domain. This potentially includes customers, employees and vendors that can receive emails from the bad actors pretending to be YOU!

What Can You Do?
At a bare minimum, your email flows (both business and marketing) should have DMARC configured to prevent spoofed emails from being delivered. TorchLight is now rolling out additional, proactive monitoring. Our Security Operations Center has seen over a 600% increase in the last three months in spoofed emails from both non-DMARC protected domains AND domains with DMARC protection in place. The TorchLight DMARC monitoring service is a real time report card showing who is sending email on your behalf, helps identify legitimate services (Google, Microsoft, Mailchimp, etc.), and whether the email messages pass the additional SPF and DKIM checks.
We consult with you during setup to confirm DMARC, DKIM and SPF records are fine tuned for security and assesses business risk, risk tolerance and other indicators to provide proactive monitoring and alerting to on-going and emergent spoofing and hijacking threats.